Gout is a metabolic disorder related to increased production or decreased excretion of uric acid in the body. We can say the direct cause of gout is caused uric acid, a byproduct generated by the breakdown of purines. In
normal people, the amount of uric acid in the blood is maintained at a
fixed 5mg% of men and 4 mg% in women, depending on age and change. To
balance the daily uric acid, uric acid is excreted mainly in the kidney
into the urine and feces, and partly through other avenues.

One reason, levels of purines in the body increases, our metabolism increases uric acid.
When the body produces too much uric acid or the acid waste too little
urine uric acid levels in the blood increased, uric acid metabolism
increases urate salts leads to the deposition of urate crystals of salt
sharp needles in the joints, cartilage, bone, held under the skin,
causing inflammation and swelling and symptoms at the deposition
location.
Causes of increased uric acid
Increased birth: disease Lesch - Nyhan: HGPT deficiency due to
increased uric acid levels from small, the disease manifests in the
body, nerve, kidney and joints. This disease is very rare and very severe.
Primary gout: a disease associated with genetic factors and atopic,
these patients have the synthesis of endogenous purines increase cause
hyperuricemia. This is also a major cause of disease.
Secondary gout: uric acid in the blood may increase secondary to the following reasons:
+ Due to consume foods containing purines (liver, heart, meat, fish, mushrooms, shrimp, crab), drink more alcohol. Actually this is only the agent has the disease rather than a direct cause.
+ Do in body enhancing endogenous purine degradation (destroying cells
and organizations) related to hematological diseases such as
polycythemia disease, may experience leucemie marrow, Hodgkin,
accounting sarcoma, multiple myeloma bone , or by the use of drugs to
kill cells treatment of melanoma.
+ Due to reduce uric acid by the kidneys: chronic nephritis, kidney
failure makes the process of reducing uric acid excretion and retention
disease.
The role of uric acid in arthritis
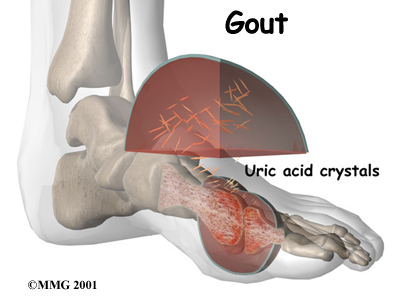
In gout , urate crystal deposition in monosodic synovial membrane will cause a series of reactions:
+ Activities Hageman factor in place thereby stimulating the
inflammatory precursor Kininogen kallicreinogen become kallicrein kinin
and inflammation in the synovium.
+ From the inflammatory response, leukocytes to focus, white blood
cells and acts of urate crystals release of leukocyte enzyme (lysozim). These enzymes are also a very strong inflammatory agent.
+
Inflammation of the synovial membrane increases metabolism, lactic acid
students in place and reduce the pH of the environment as they attempt
more urate deposition and inflammation here to become a continuous
closed loop inflammation lasts.
Therefore, the fact that the two could gout: Can gout, acute
inflammatory process going on in a short time and then terminate, or
recurrence. Can chronic gout urate deposition process and prolonged, continuous expression of inflammatory will not stop.

0 comments:
Đăng nhận xét